PlAwAnSaI
Administrator


















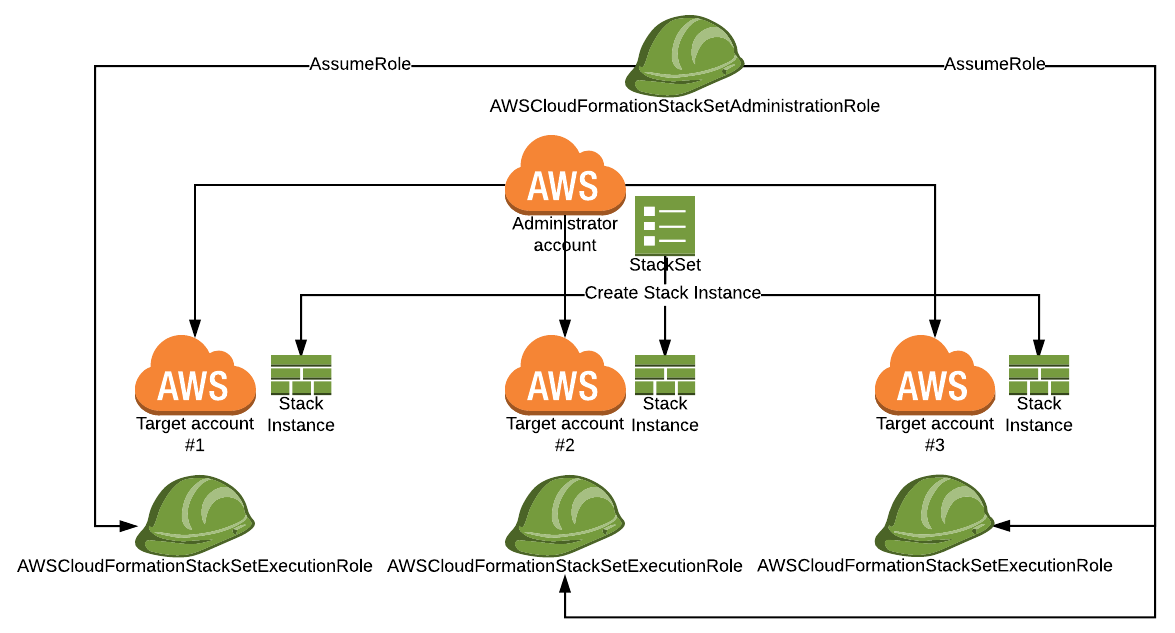
- An Application team has asked a SysOps Admin to provision an additional environment for an application in four additional regions. The application is running on more than 100 instances in us-east-1, using fully baked AMIs. An AWS CloudFormation template has been created to deploy resources in us-east-1. To provision the application quickly the SysOps Admin must Run the existing CloudFormation template in each additional region based on the success of the template used currently in us-east-1.
- A company has a fleet of EC2 instances, and needs to remotely execute scripts for all of the instances. Amazon EC2 System Manager Run Command allows this.
- A company is creating an application that will keep records. The application will run on Amazon EC2 instances and will use an Amazon Aurora MySQL DB as its data store. To maintain compliance, the application must not retain information that is determined to be sensitive. To detect if sensitive data is being stored in the application a SysOps admin should Export data from the DB by using an AWS Lambda function. Store the data in Amazon S3. Use Amazon Macie to examine the stored data. Examine the report for any sensitive data that is discovered.
- Access Control List (ACL) is the document that defines who can access a particular bucket or object in Amazon S3. ACLs enable to manage access to buckets and objects. Each bucket and object has an ACL attached to it as a subresource. It defines which AWS accounts or groups are granted access and the type of access.
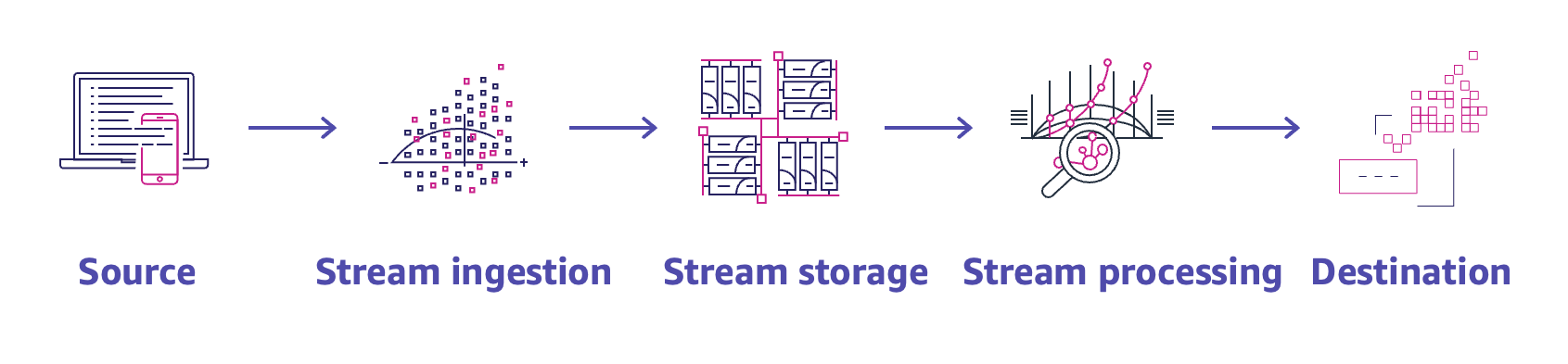
- A user is sending custom data metrics to CloudWatch. The allowed time stamp granularity for each data point published for the custom metric is 1 millisecond (ms).
The user is allowed to send data up to 1,000 of a second. CloudWatch aggregates the data by each minute and generates a metric for that.
- Dev teams are maintaining several workloads on AWS. Company management is concerned about rising costs and wants the SysOps Admin to configure alerts so teams are notified when spending approaches preset limits. AWS Budgets service will satisfy these requirements.
- A company has several accounts between different teams and wants to increase its auditing and compliance capabilities. The accounts are managed through AWS Organizations. Management wants to provide the security team with secure access to the account logs while also restricting the possibility for the logs to be modified. A SysOps admin can achieve this with the LEAst amount of operational overhead by From the master account, create an organization trail using AWS CloudTrail and apply it to all Regions. Use IAM roles to restrict access.
- A launch configuration in Auto Scaling represents a template that the Auto Scaling group uses to launch the Amazon EC2 instances. When create a launch configuration, specify information for the instances such as the ID of the Amazon Machine Image (AMI), the instance type, a key pair, one or more security groups, and a block device mapping.
- AWS CloudWatch is a service used to monitor the AWS resources and the applications running on EC2. It collects and tracks the metrics of various services or applications.
- A Dev team recently deployed a new version of a web application to production. After the release, penetration testing revealed a cross-site scripting vulnerability that could expose user data. AWS WAF service will mitigate this issue.
- Every object in Amazon S3 is stored in a Bucket. Before can store data in Amazon S3, must create a bucket.
- An Auto Scaling group scales up and down based on Average CPU Utilization. The alarm is set to trigger a scaling event when the Average CPU Utilization exceeds 80% for 5 minutes. Currently, the Average CPU has been 95% for over two hours and new instances are not being added. The issue could be The maximum size of the Auto Scaling group is below or at the current group size.
- AWS CloudWatch supports the custom metrics. The user can always capture the custom data and upload the data to CloudWatch using CLI or APIs. The user has to always include the namespace as a part of the request. However, the other parameters are optional. If the user has uploaded data using CLI, he can view it as a graph inside the console. The data will take around 2 minutes to upload but can be viewed only after around 15 minutes.
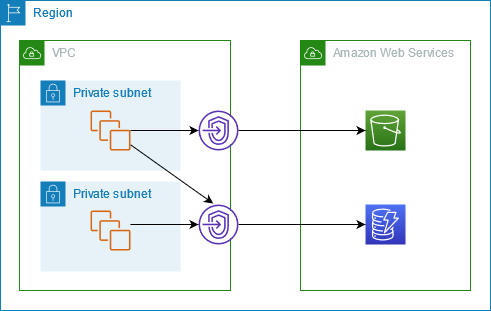
- A popular auctioning platform requires near-real-time access to dynamic bidding information. The platform must be available at all times. The current Amazon RDS instance often reaches 100% CPU utilization during the weekend auction and can no longer be resized. To improve application performance, a sysops admin is evaluating Amazon ElastiCache, and has chosen Redis (cluster mode enabled) instead of Memcached. Reasons for making this choice are Multi-AZ with automatic failover and Online resharding.
Amazon ElastiCache for Redis supports both Redis cluster and non-cluster modes and provides high availability via support for automatic failover by detecting primary node failures and promoting a replica to be primary with minimal impact.
- Amazon S3 offer Storage over the Internet. It's a simple web services interface that can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web.
- To change the Instance type for instances running. In application tier that are using Auto Scaling. Would change the instance type definition in Auto Scaling launch configuration.
- To generate a report detailing specific cost allocation tags when creating a Monthly Cost Allocation report required steps are:
- Activate the 'requested' tags by clicking Manage report tags on the Billing Preferences page.
- Select the checkbox for Cost Allocation Report in the AWS account's Billing Management Console.
Last edited: