PlAwAnSaI
Administrator
CCNP คือ Cisco Certified Network Professional เป็นระดับของ มืออาชีพ ที่มีความสามารถพอสมควรในการสนับสนุน ติดตั้ง รวมถึงการแก้ปัญหาต่างๆ ด้าน Routing และ Switching ที่ใช้ใน Network ทั่วไป
ต้องสอบ 2 วิชา วิชาหลัก และวิชาเลือก ไม่ต้องมี CCNA ก็สอบได้ถ้าเก๋าพอ ซึ่งถ้าสอบในระดับ Professional หรือ Specialist จะเป็นการ Recertificate ในระดับ Associate ไปในตัว ดังนั้นรายวิชา CCNP แต่ละตัว ไม่ควรทิ้งให้นานเกินไป เพราะเทคโนโลยีมันพัฒนาไปเรื่อยๆ มันจะมีเรื่องใหม่ๆ มาให้เราศึกษาเรื่อยๆ แล้วก็เราไม่มีทางรู้ว่า Cisco จะประกาศยกเลิกข้อสอบแต่ละตัวเมื่อไหร่ (ยกตัวอย่างวิชา ROUTE กับ SWITCH ในระดับ CCNP ที่ยกเลิกไปแล้ว)
CCNP SWITCH 642-813
CCNP TSHOOT 642-832
Cisco CCNP & CCIE Enterprise Core - ENCOR 350-401:

Enterprise Networks Design Principles:

ต้องสอบ 2 วิชา วิชาหลัก และวิชาเลือก ไม่ต้องมี CCNA ก็สอบได้ถ้าเก๋าพอ ซึ่งถ้าสอบในระดับ Professional หรือ Specialist จะเป็นการ Recertificate ในระดับ Associate ไปในตัว ดังนั้นรายวิชา CCNP แต่ละตัว ไม่ควรทิ้งให้นานเกินไป เพราะเทคโนโลยีมันพัฒนาไปเรื่อยๆ มันจะมีเรื่องใหม่ๆ มาให้เราศึกษาเรื่อยๆ แล้วก็เราไม่มีทางรู้ว่า Cisco จะประกาศยกเลิกข้อสอบแต่ละตัวเมื่อไหร่ (ยกตัวอย่างวิชา ROUTE กับ SWITCH ในระดับ CCNP ที่ยกเลิกไปแล้ว)
- เจาะเนื้อหาและหัวข้อ CCNA ใหม่ และ CCNP Enterprise:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=ucgSn8fJBUU
- Free CCNP 350-401 ENCOR Complete Coursewww.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLAqaqJU4wzYVS_QYH1_LEh5VLDu-Oaiwy
www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLhfrWIlLOoKPM3poHlHLpw-b6cigthng2 - CCNP Enterprise -350-401-ENCOR- Cisco Core Technologies
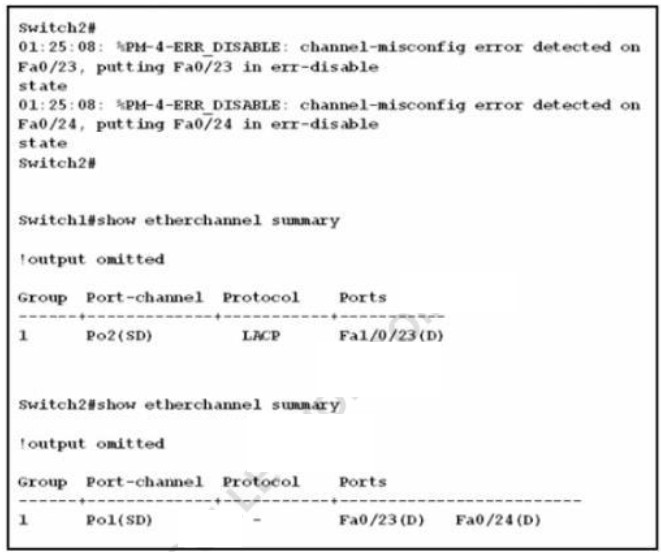
www.udemy.com/course/ccnp-enterprise-300-401-implementing-cisco-enterprise-core - อธิบายการทำงาน และ การตั้งค่า Ether-channel:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=waA-kTBevQ4 - [CCNP ENCOR] Basic BGP and Configuration:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=y6YtCyMBhKY - [CCNP ENCOR] Introducing to Multiple Spanning-Tree (MSTP):www.youtube.com/watch?v=TxSLRuQP2bY
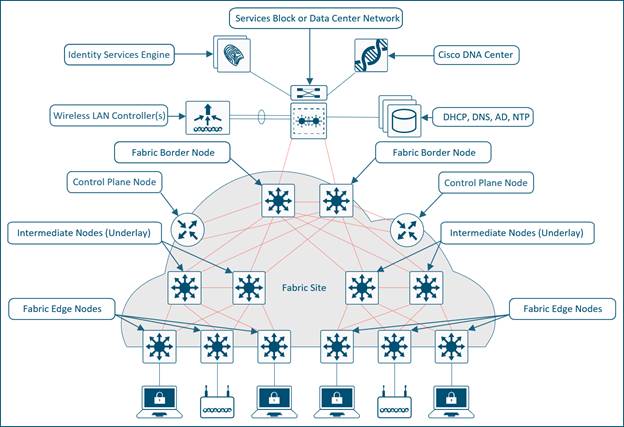
- Introducing to Cisco DNA Center:www.youtube.com/watch?v=XaZZgOKPnG0
- Describe SD-Access from Cisco CCNP Enterprise ENCOR (350-401):
www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7_0On3pcY4
=AT3aVOy8QE8ED1-JqpFKThTgoz8sbhh2WYtDY7P4SEXJDLZ-9EVaDnDOvxDnaShqTp-PvxGbl8no9VKIjSUX7BFVtiayGaD6L__EIdDyv0H3D4VJLMwzZBg_-FIi2zW6kVVT8h-HObx15CuHhxS85L1EVLRWiaRRWYZ0jc1orA7sc0QiCrAhpMp5LrxS0Ol8s4hdXvTY t=_blank] - CCNP Cisco Networking Academy Version v5.0:
forum.siamnetworker.com/?topic=294
- ประสบการณ์การเตรียมตัวสอบ CCNP:
zone-network.blogspot.com/2014/06/ccnp.html
CCNP SWITCH 642-813
CCNP TSHOOT 642-832
Cisco CCNP & CCIE Enterprise Core - ENCOR 350-401:
- Starting from February 24th - 2020
- Exam Cost: 400$
- Exam Center: Pearson Vue
- NO Prerequisites
- Acquired Badges: Cisco Certified Specialist - Enterprise Core
- Enrollment: Cisco CCNP Enterprise & Cisco CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure
- Recertify CCNA 200-301 & CCNP
- Expires: 3 years
- CCNP Enterprise: ENCOR + Concentration Exam:

- Shared Topics with CCNA 200-301:
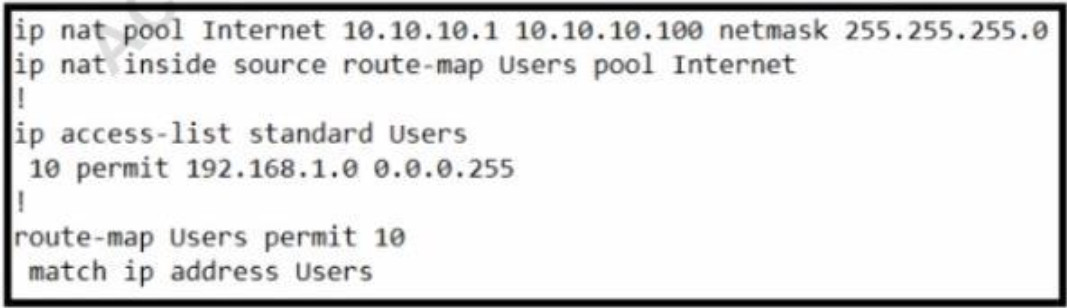
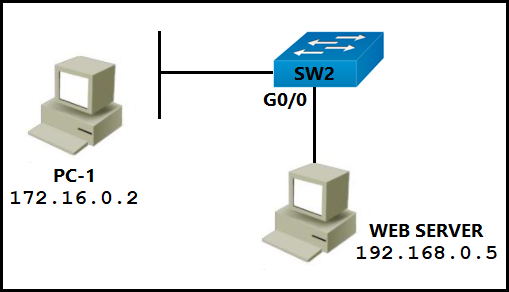
- Design, Virtualization, WLAN, STP, NTP, NAT, ACL
- https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/encor-exam-topics
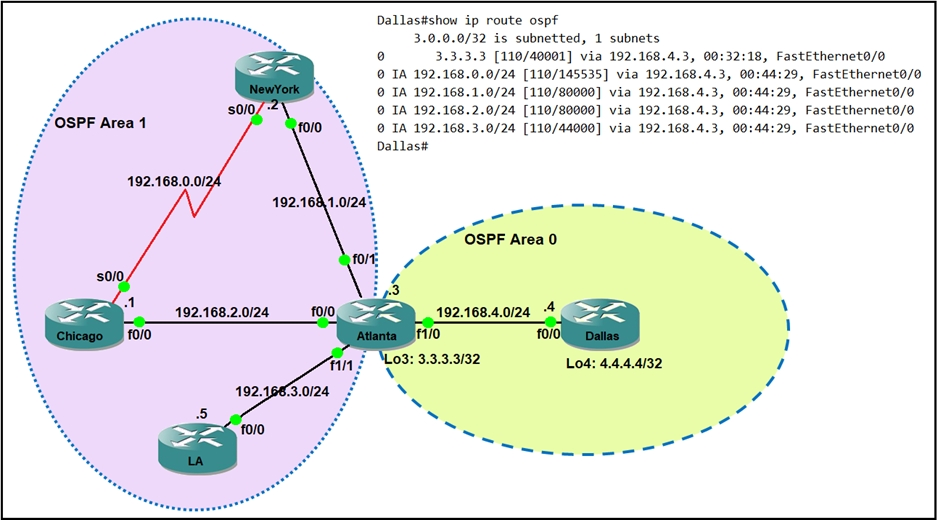
Enterprise Networks Design Principles:
- Tier 2, Tier 3, and Fabric Capacity Planning
- Simplify Scaling & Troubleshooting
- Depends on network size, and future growing