PlAwAnSaI
Administrator
Introducing the OSPF Protocol
Link-State Protocols

Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) ถือเป็น Routing Protocol ตัวนึงที่นิยมกันอย่างแพร่หลายมากที่สุดในระบบ Network เนื่องจากมีจุดเด่นในหลายด้าน เช่น การที่ตัวมันเป็น Routing Protocol แบบ Link State, การที่มี Algorithm ในการค้นหาเส้นทางด้วยตัวเอง ซึ่งเปรียบเสมือนว่า ตัวของ Router ที่ Run OSPF ทุกตัวเป็น Root หรือจุดเริ่มต้นของระบบไปยังกิ่งย่อยๆ หรือ Node ต่างๆ ซึ่งเป็น Technique ในการลดเส้นทางที่วน Loop (Routing Loop) ของ Routing ได้เป็นอย่างดี รวมถึงความสามารถในการ Convergence หรือการรับรู้ถึงความเปลี่ยนแปลงใน Topology หรือเส้นทางของ Network ได้อย่างรวดเร็วจนกระทั่งพูดได้เลยว่า แทบจะทันทีที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง Topology ขึ้นในระบบ และความสามารถในการรองรับการขยายของระบบ (Scalable) ได้อย่างดีเยี่ยม ซึ่งข้อดีดังกล่าวนั้น ทำให้บรรดา Network Architect ต่างๆ นั้นนิยมเลือก OSPF มาเป็น Routing Protocol หลัก แทนที่ Routing Protocol แบบ Distance Vector เช่น RIP หรือ IGRP ซึ่งก่อนที่จะลงถึงรายละเอียดของ OSPF นั้น ก็จะมีการเกริ่นถึง คำที่เกี่ยวข้องภายใน Routing Protocol ของ OSPF เสียก่อน
Link-State Data Structures:
ความแตกต่างระหว่าง Link State Routingและ (vs.) Distance Vector Routing:
OSPF Areas characteristics:

Link-State Protocols

Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) ถือเป็น Routing Protocol ตัวนึงที่นิยมกันอย่างแพร่หลายมากที่สุดในระบบ Network เนื่องจากมีจุดเด่นในหลายด้าน เช่น การที่ตัวมันเป็น Routing Protocol แบบ Link State, การที่มี Algorithm ในการค้นหาเส้นทางด้วยตัวเอง ซึ่งเปรียบเสมือนว่า ตัวของ Router ที่ Run OSPF ทุกตัวเป็น Root หรือจุดเริ่มต้นของระบบไปยังกิ่งย่อยๆ หรือ Node ต่างๆ ซึ่งเป็น Technique ในการลดเส้นทางที่วน Loop (Routing Loop) ของ Routing ได้เป็นอย่างดี รวมถึงความสามารถในการ Convergence หรือการรับรู้ถึงความเปลี่ยนแปลงใน Topology หรือเส้นทางของ Network ได้อย่างรวดเร็วจนกระทั่งพูดได้เลยว่า แทบจะทันทีที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง Topology ขึ้นในระบบ และความสามารถในการรองรับการขยายของระบบ (Scalable) ได้อย่างดีเยี่ยม ซึ่งข้อดีดังกล่าวนั้น ทำให้บรรดา Network Architect ต่างๆ นั้นนิยมเลือก OSPF มาเป็น Routing Protocol หลัก แทนที่ Routing Protocol แบบ Distance Vector เช่น RIP หรือ IGRP ซึ่งก่อนที่จะลงถึงรายละเอียดของ OSPF นั้น ก็จะมีการเกริ่นถึง คำที่เกี่ยวข้องภายใน Routing Protocol ของ OSPF เสียก่อน
Link-State Data Structures:
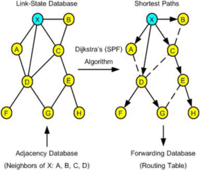
- Neighbor Table: ไว้เก็บรายชื่อ Router ที่ Form ความสัมพันธ์ และสถานะของ DR/BDR และสถานะของ Link, Hello และ Dead Time Interval
- Designated Router (DR) - เป็น Router ที่เป็นจุดศูนย์กลางในการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลหรือสถานะระหว่าง Router ด้วยกัน เนื่องจากการมี Router ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็น Centralize ในระบบ จะสามารถช่วยลดปริมาณ Packet LSA ที่จะส่งกันระหว่าง Router ด้วยกันได้ ซึ่ง DR นี้ จะถูกใช้ใน Network ที่เป็น Broadcast (Multi-Access) และ Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (เช่น Ethernet หรือ Frame-Relay เท่านั้น)
- Backup Designated Router (BDR) - จะถือว่าเป็น Router ตัวแทน (Hot Stanby) ของ Designated Router (DR) โดยที่ BDR จะคอยรับ Routing Update จาก Router เพื่อนบ้าน แต่ตัวมันเองจะไม่ทำการ Flood LSA ออกไปเหมือนอย่างที่ DR ทำ จนกระทั่งหากว่า DR ในระบบล่มลงไป BDR จึงจะเข้ามาเป็น DR แทน
- Also knows as the adjacency database
- Contains list of recognized neighbors
- Topology Table: ไว้เก็บเส้นทางที่เป็นไปได้ทั้งหมดในการที่ Router จะส่ง Packet ไปยังปลายทาง ซึ่งใน OSPF สามารถที่จะทำการกระจายโหลด (Load Balance) ไปยังเส้นทางที่มี Cost เท่ากันได้ 6 เส้นทาง (4 เส้นทางโดยค่า Default)
- Typically referred to as LSDB
- Contains all routers and their attached links in the area or network
- Identical LSDB for all routers within an area
- Routing Table: ไว้เก็บเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดที่ได้รับการคำนวณมาจาก SPF Algorithms เรียบร้อยแล้ว
- Commonly named a forwarding database
- Contains list of best paths to destinations
ความแตกต่างระหว่าง Link State Routingและ (vs.) Distance Vector Routing:
- รู้เส้นทางทั้งหมดใน Network จากแผนภาพ Topology ของตนใน Topology Table
- Each router has a full picture of the topology.
- Consequently, link-state routers tend to make more accurate decisions. vs.
- คำนวณเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดผ่านทาง SPF Algorithms ของตนเอง vs.
ส่ง Packet ผ่านเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดที่ Router เพื่อนบ้านประกาศออกมา
- Update เฉพาะเมื่อมีการเปลี่ยนแปลง Topology เท่านั้น (Triggered Update) และ Speed ในการ Converged ที่เร็วมาก vs.
Update Routing Table เป็นระยะๆ และมีการเข้าสู่สภาวะคงที่ (Converged) ที่ช้า
- ส่งสถานะของ Link ตนเอง ออกไปให้ Router เพื่อนบ้าน vs.
ส่งตาราง Routing Table ทั้งตารางออกไปให้ Router เพื่อนบ้าน
- Link-state routers recognize more information about the network than their distance vector counterparts.
- สนับสนุนการแบ่ง Network เป็นลำดับขั้น (Hierarchical Network)
- ใช้ Algorithm ของ Diijkstra (Link State) ในการค้นหาเส้นทาง และป้องกัน Routing Loop
- สนับสนุน Classless Routing และ CIDR (Classless Interdomain Routing)
- สามารถทำ Route Summarization เพื่อลดขนาดของ Routing Table ได้
- Routing Update สามารถที่จะควบคุมการส่งได้ ไม่เหมือน Routing Protocol แบบ Distance Vector ที่ต้องส่ง Routing Table ทั้งตารางออกไป ตามช่วงเวลาที่กำหนด ทำให้สูญเสีย Bandwidth ไปโดยไม่จำเป็น
- ในการส่ง Routing Update จะทำผ่าน Multicast Address ซึ่งมีข้อดี คือลดผลกระทบต่อ Host หรือ Client อื่นๆ จากการ Broadcast
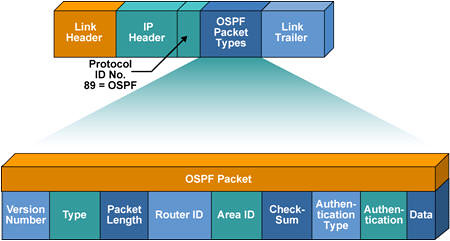
- สนับสนุนการทำ Authentication ทั้งแบบ Clear Text และ MD5
- Instances หรือ Process ของ OSPF สามารถเริ่มได้ตั้งแต่ 1 - 65,535 แต่ไม่สมควร Run OSPF มากกว่า 1 Process พร้อมๆ กัน หากไม่จำเป็น
- Area ของ OSPF สามารถมีได้ถึง 2^32 หรือประมาณ 4,200,000 Area
- ใน Router ที่ Run OSPF จะต้องมี Area 0 อยู่เสมอ ถือว่าเป็น Backbone Area
- หากกว่า Network นั้นๆ มีหลาย Area ทุกๆ Area จะต้อง Connect เข้าหา Area 0 เสมอ อาจจะเป็นการต่อ Interface เข้าหา Area 0 หรือทำ Virtual Links วิ่งเข้าหา Area 0 ก็ได้
- Default Administrative Distance ของ OSPF คือ 110
- Link-state routing requires a hierachical network structure that is enforced by OSPF
- This two-level hierarchy consists of the following:
- Transit area (backbone or area 0)
- Regular areas (non-backbone areas)
OSPF Areas characteristics:
- Minimizes routing table entries - ลดปริมาณหน่วยความจำที่ใช้ในการจัดเก็บ Routing Table เพราะตาราง Routing Table ที่เกิดขึ้นบน Router แต่ละตัวสามารถได้รับการปรับแต่งให้มีขนาดเล็กลงได้ ด้วยการ Configure route summarization บน Router ตัวริมที่เชื่อมต่อระหว่าง Area หรือเรียกว่า Area Border Router (ABR)
- Localizes impact of a topology change within an area - จำกัดความถี่ในการคำนวณ Algorithm SPF ใหม่ เมื่อมีการเปลี่ยนแปลง Topology ของ Router แต่ละตัว เพราะ Router จะคำนวณอัลกอริทึม SPF ใหม่ ก็ต่อเมื่อได้รับ LSA Update จาก Router ภายใน Area เดียวกันเท่านั้น การคำนวณ SPF ใหม่จะมีผลต่อภาระ Load ของ CPU ของ Router
- Detailed LSA flooding stops at the area boundary - จำกัดปริมาณ Packet ที่เกิดขึ้นอันเนื่องมาจากการส่ง LSA Update ให้อยู่ภายในขอบเขตของ Area เดียวกัน (LSA Update จะไม่ถูกส่งข้ามไป Area อื่น)
- Requires a hierarchical network design